Best root canal treatment for children in pune
Best root canal treatment in pune
Root canal treatment, or endodontic therapy, in children is a specialized procedure aimed at saving a tooth that has become severely damaged or infected. Although the principles are similar to those in adults, there are some specific considerations and approaches when performing root canal treatments on children. Here’s a comprehensive overview:
What is Root Canal Treatment?
Root canal treatment involves removing the damaged or infected pulp (the soft tissue inside the tooth), cleaning and disinfecting the root canals, and then sealing them to prevent future infection. This procedure helps preserve the tooth and maintain its function.
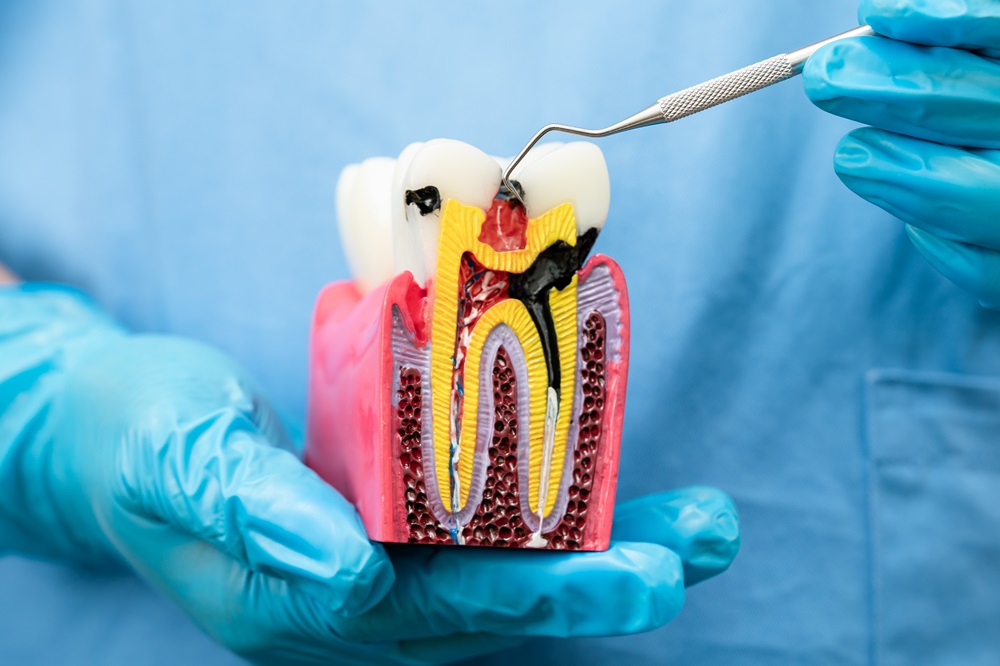
Why is Root Canal Treatment Needed in Children?
1. Severe Decay: Extensive tooth decay can reach the pulp, causing infection or abscesses.
2. Trauma: Injury to the tooth, such as a fracture or a blow, can damage the pulp and necessitate treatment.
3. Pulpitis: Inflammation of the pulp tissue due to deep cavities or repeated dental procedures.
Differences in Treatment for Children
1. Tooth Type: Primary (baby) teeth and permanent teeth differ in their treatment approaches. In primary teeth, the goal is often to preserve the tooth until it naturally falls out, whereas for permanent teeth, the focus is on long-term preservation.
2. Treatment Duration: Root canals on primary teeth are typically simpler and might require fewer visits compared to those on permanent teeth.
3. Tooth Development: In young children, the roots of primary teeth are still developing. Special techniques might be used to ensure proper treatment without damaging the developing permanent tooth underneath.
Procedure Overview
1. Diagnosis: The dentist performs a thorough examination, including X-rays, to assess the extent of damage or infection and determine if a root canal is necessary.
2. Local Anesthesia: The affected tooth and surrounding area are numbed with a local anesthetic to minimize discomfort during the procedure.
3. Access Opening: The dentist makes a small opening in the crown of the tooth to access the pulp chamber and root canals.
4. Pulp Removal: The damaged or infected pulp is carefully removed from the root canals.
5. Cleaning and Shaping: The canals are cleaned and shaped to remove debris and disinfect the area.
6. Filling: The cleaned canals are filled with a biocompatible material, usually gutta-percha, to seal them and prevent future infections.
7. Restoration: The tooth is then restored with a filling or a crown to restore its function and appearance. In primary teeth, a crown is often used to provide extra protection.
Post-Treatment Care
1. Pain Management: Some discomfort or mild pain is normal after the procedure. Analgesics (Pain killers) can help manage this, but follow-up with the dentist is essential if pain persists.
2. Oral Hygiene: Maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial to ensure the health of the treated tooth and overall dental health.
3. Diet: Avoid hard or sticky foods for a few days after the procedure to prevent damage to the restored tooth.
4. Follow-Up: Regular follow-up visits are important to monitor the tooth and ensure that healing is proceeding as expected.




